Mole Going From Flat to Bumpy to Flat Again
What is a common mole?
A mutual mole is a growth on the peel that develops when pigment cells (melanocytes) grow in clusters. Most adults accept betwixt 10 and 40 common moles. These growths are usually plant in a higher place the waist on areas exposed to the lord's day. They are seldom found on the scalp, breast, or buttocks.
Although common moles may be present at nascence, they usually announced later in childhood. Most people continue to develop new moles until about age 40. In older people, common moles tend to fade away.
Some other name for a mole is a nevus. The plural is nevi.
What does a common mole wait like?
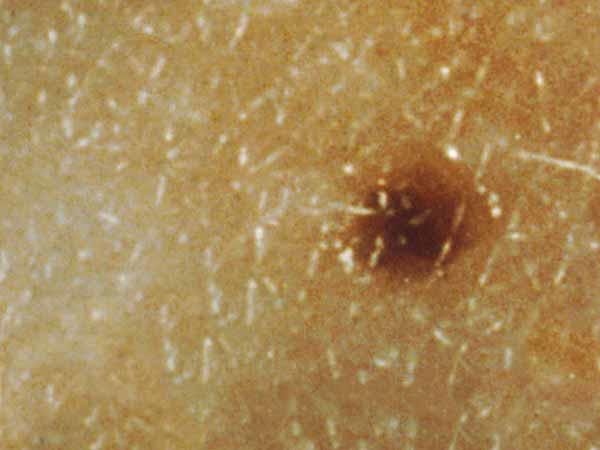
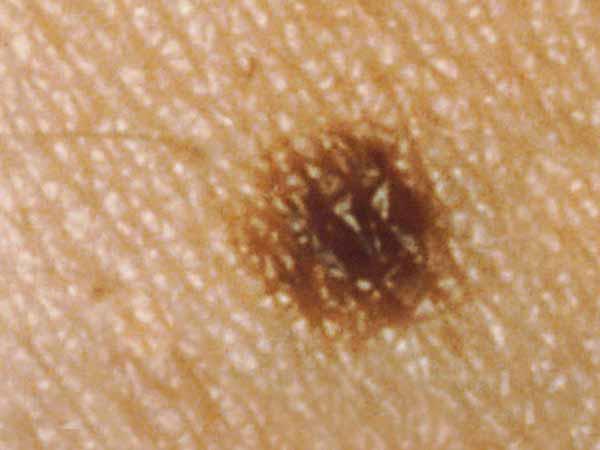
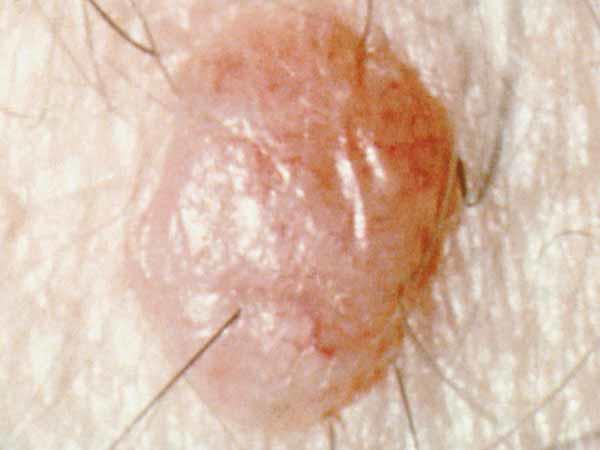
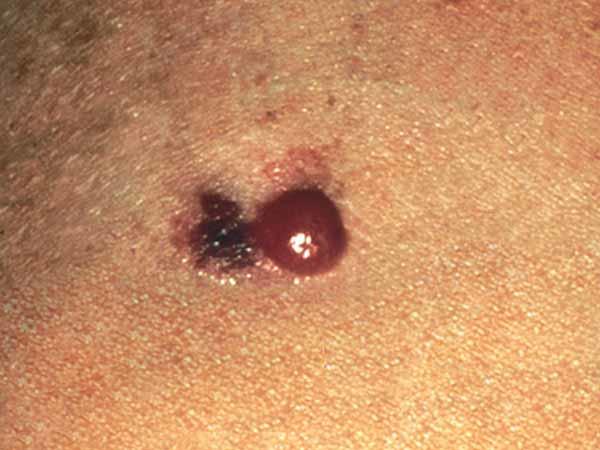
A common mole is normally smaller than about 5 millimeters wide (about 1/4 inch, the width of a pencil eraser). It is round or oval, has a smooth surface with a distinct edge, and is often dome-shaped. A common mole usually has an even color of pinkish, tan, or dark-brown. People who have dark skin or hair tend to have darker moles than people with off-white skin or blonde hair. Several photos of common moles are shown hither, and more photos are available on the What Does a Mole Look Like? page.
Can a common mole turn into melanoma?
Yes, but a common mole rarely turns into melanoma, which is the almost serious type of skin cancer.
Although mutual moles are not cancerous, people who have more than l mutual moles take an increased chance of developing melanoma (i).
People should tell their dr. if they notice any of the post-obit changes in a mutual mole (ii):
- The color changes.
- The mole gets unevenly smaller or bigger (different normal moles in children, which become evenly bigger).
- The mole changes in shape, texture, or height.
- The pare on the surface becomes dry or scaly.
- The mole becomes hard or feels lumpy.
- Information technology starts to itch.
- It bleeds or oozes.
What is a dysplastic nevus?
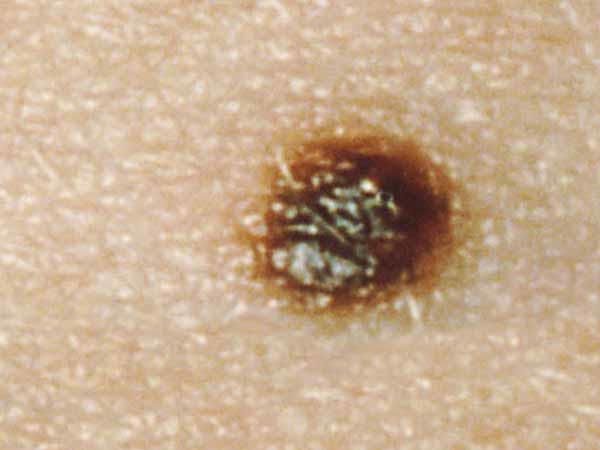
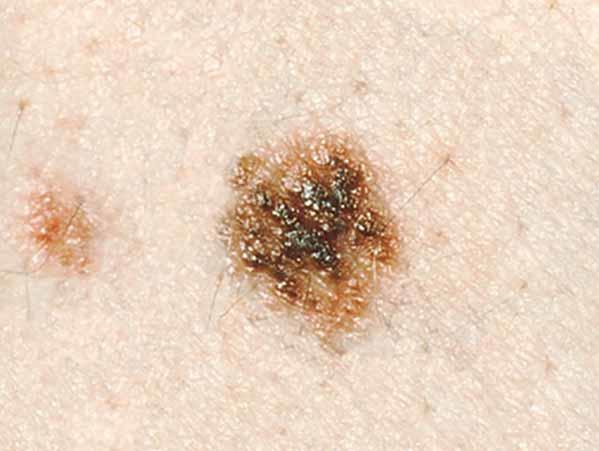
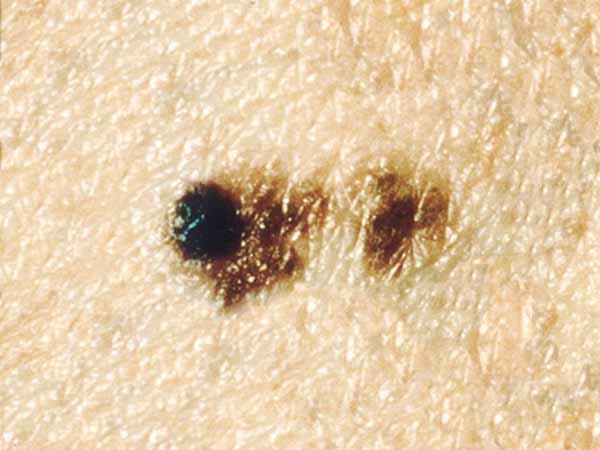
A dysplastic nevus is a type of mole that looks different from a common mole. (Some doctors use the term "atypical mole" to refer to a dysplastic nevus.) A dysplastic nevus may be bigger than a common mole, and its colour, surface, and edge may be dissimilar. It is commonly more 5 millimeters broad (1, 3). A dysplastic nevus can accept a mixture of several colors, from pink to dark brown. Usually, it is flat with a smooth, slightly scaly, or pebbly surface, and information technology has an irregular edge that may fade into the surrounding pare. Some examples of dysplastic nevi are shown here. More than examples are on the What Does a Mole Look Like? page.
A dysplastic nevus may occur anywhere on the body, only it is unremarkably seen in areas exposed to the sunday, such as on the dorsum. A dysplastic nevus may besides appear in areas not exposed to the sunday, such equally the scalp, breasts, and areas below the waist (1, 3). Some people take only a couple of dysplastic nevi, but other people have more than 10. People who take dysplastic nevi usually too have an increased number of mutual moles.
Tin a dysplastic nevus plough into melanoma?
Yes, but almost dysplastic nevi do not plough into melanoma (1, 3). Nigh remain stable over fourth dimension. Researchers estimate that the chance of melanoma is about ten times greater for someone with more than than v dysplastic nevi than for someone who has none, and the more than dysplastic nevi a person has, the greater the risk of developing melanoma (1, three).
What should people practise if they have a dysplastic nevus?
Everyone should protect their skin from the sun and stay away from sunlamps and tanning booths, merely for people who accept dysplastic nevi, information technology is even more of import to protect the skin and avert getting a suntan or sunburn.
In add-on, many doctors recommend that people with dysplastic nevi check their skin once a month (2, 4). People should tell their doctor if they encounter whatsoever of the following changes in a dysplastic nevus (2):
- The colour changes.
- It gets smaller or bigger.
- It changes in shape, texture, or height.
- The peel on the surface becomes dry or scaly.
- It becomes hard or feels lumpy.
- It starts to itch.
- It bleeds or oozes.
Another affair that people with dysplastic nevi should do is get their skin examined past a doctor (2, 4). Sometimes people or their doctors take photographs of dysplastic nevi so changes over fourth dimension are easier to come across (2). For people with many (more than five) dysplastic nevi, doctors may conduct a skin exam once or twice a year because of the moderately increased risk of melanoma. For people who likewise have a family history of melanoma, doctors may advise a more than frequent peel test, such as every 3 to 6 months (3).
Should people accept a doctor remove a dysplastic nevus or a common mole to forbid it from irresolute into melanoma?
No. Normally, people do non need to have a dysplastic nevus or common mole removed. One reason is that very few dysplastic nevi or common moles turn into melanoma (i, 3). Another reason is that even removing all of the moles on the skin would not prevent the evolution of melanoma because melanoma can develop as a new colored area on the skin (2). That is why doctors usually remove only a mole that changes or a new colored expanse on the pare.
What is melanoma?
Melanoma is a blazon of skin cancer that begins in melanocytes. Information technology is potentially unsafe because it tin can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the torso, such as the lung, liver, bone, or brain. The earlier that melanoma is detected and removed, the more likely that handling will be successful.
Well-nigh melanocytes are in the peel, and melanoma can occur on whatsoever peel surface. It tin can develop from a common mole or dysplastic nevus, and it tin likewise develop in an surface area of apparently normal skin. In addition, melanoma can also develop in the eye, the digestive tract, and other areas of the body.
When melanoma develops in men, information technology is oft found on the head, cervix, or back. When melanoma develops in women, it is often plant on the dorsum or on the lower legs.
People with dark skin are much less likely than people with fair skin to develop melanoma. When it does develop in people with nighttime skin, it is often establish under the fingernails, nether the toenails, on the palms of the easily, or on the soles of the feet.
What does melanoma look like?
Often the commencement sign of melanoma is a change in the shape, colour, size, or experience of an existing mole. Melanoma may also appear as a new colored area on the skin.
The "ABCDE" rule describes the features of early melanoma (2, v):
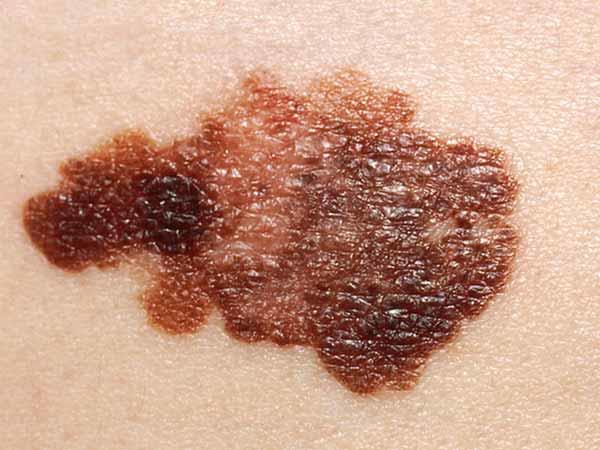
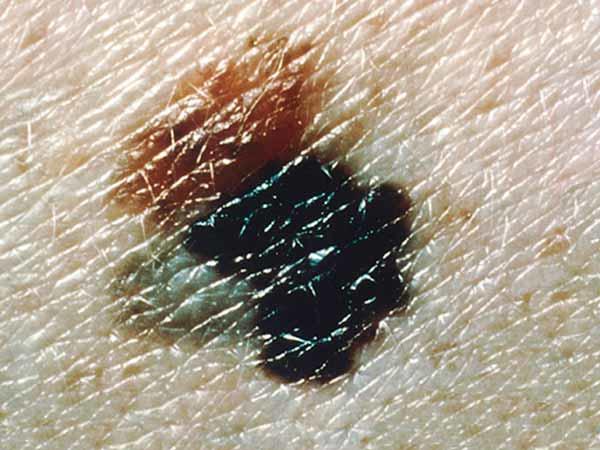
- Disproportion . The shape of one half does non match the other half.
- Edge that is irregular . The edges are often ragged, notched, or blurred in outline. The pigment may spread into the surrounding peel.
- Colour that is uneven . Shades of black, brown, and tan may be nowadays. Areas of white, grayness, red, pink, or blue may also be seen.
- Diameter . There is a alter in size, usually an increase. Melanomas tin be tiny, but most are larger than six millimeters wide (about 1/iv inch wide).
- Evolving . The mole has changed over the past few weeks or months.
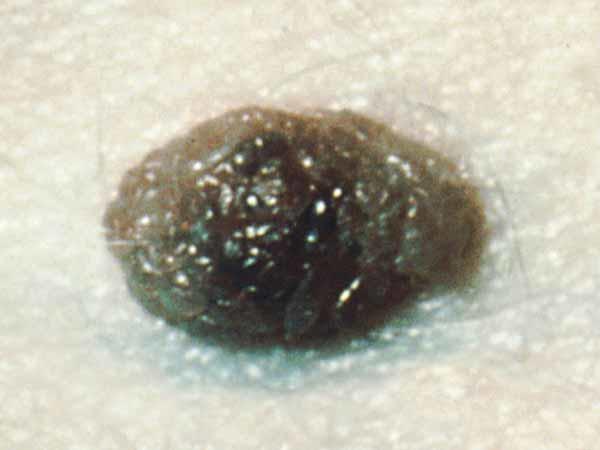
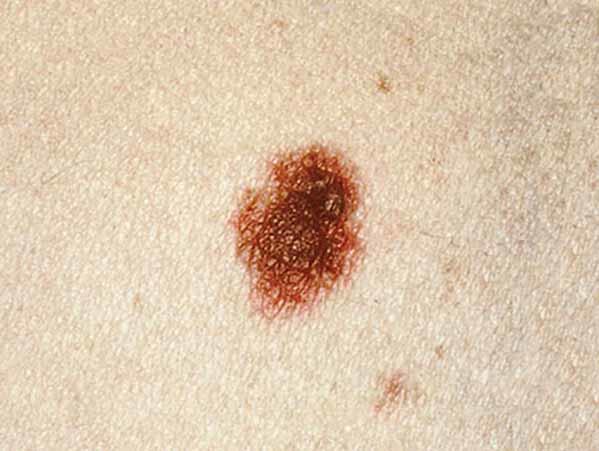
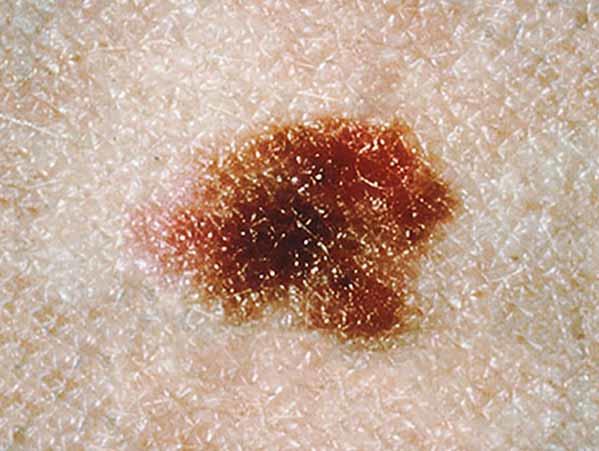
Melanomas can vary greatly in how they look. Many testify all of the ABCDE features. However, some may show but ane or ii of the ABCDE features (5). Several photos of melanomas are shown here. More photos are on the What Does Melanoma Look Like? page.
In avant-garde melanoma, the texture of the mole may change. The skin on the surface may break down and look scraped. It may become hard or lumpy. The surface may ooze or drain. Sometimes the melanoma is itchy, tender, or painful.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
The only way to diagnose melanoma is to remove tissue and check it for cancer cells. The dr. will remove all or part of the skin that looks abnormal. Unremarkably, this procedure takes only a few minutes and can be done in a doctor's office, clinic, or hospital. The sample will be sent to a lab and a pathologist will look at the tissue under a microscope to check for melanoma.
What are the differences betwixt a common mole, a dysplastic nevus, and a melanoma?
Common moles, dysplastic nevi, and melanoma vary past size, color, shape, and surface texture. The list beneath summarizes some differences betwixt moles and cancer. Another of import difference is that a mutual mole or dysplastic nevus will not return after it is removed by a full excisional biopsy from the skin, but melanoma sometimes grows dorsum. As well, melanoma can spread to other parts of the trunk.
Common Mole (Nevus)
- Is it cancer? No. Common moles rarely become cancer.
- How many people accept common moles? Most Americans—about 327 meg people—accept common moles.
- How big are they? Normally less than 5 millimeters wide, or almost 1/4 inch (not as wide as a new pencil eraser).
- What color are they? May exist pink, tan, brownish, blackness (in people with nighttime skin), or a color that is very close to a person's normal skin tone. The color is usually even throughout.
- What shape are they? Usually round or oval. A common mole has a distinct edge that separates information technology from the rest of the skin.
- What is the surface texture? Begins as a apartment, smooth spot on the skin. May get raised and form a smoothen crash-land.
Dysplastic Nevus
- Is information technology cancer? No. A dysplastic nevus is more likely than a mutual mole to become cancer, but about do non become cancer.
- How many people accept dysplastic nevi? Almost 1 in x Americans—about 33 meg people—have at least one dysplastic nevus (3, 4, 6–8).
- How large are they? Often wider than v millimeters (wider than a new pencil eraser).
- What color are they? May be a mixture of tan, brown, and scarlet or pink shades.
- What shape are they? Accept irregular or notched edges. May fade into the residual of the peel.
- What is the surface texture? May accept a shine, slightly scaly, or rough, irregular, and pebbly appearance.
Melanoma
- Is it cancer? Yep.
- How many people have melanoma? Melanoma is much less common than other kinds of skin cancer. But every year, about 2 in 10,000 Americans develop melanoma (9). In 2018, an estimated 91,270 new cases of melanoma volition be diagnosed in the Usa (10). In January 2015, more than 1.2 1000000 people in the United States were living with melanoma of the skin (9).
- How big are they? Usually wider than 6 millimeters (wider than a new pencil eraser).
- What color are they? Normally uneven in colour. May have shades of blackness, brown, and tan. May also have areas of white, gray, red, pinkish, or blue.
- What shape are they? Ofttimes irregular and asymmetrical (the shape of ane half does non match the other one-half). Edges may be ragged, notched, or blurred. May fade into the rest of the skin.
- What is the surface texture? May intermission down and await scraped, become difficult or lumpy, or ooze or bleed.
What should people exercise if a mole changes, or they find a new mole or some other alter on their peel?
People should tell their doctor if they find a new mole or a change in an existing mole. A family doctor may refer people with an unusual mole or other concerns about their skin to a dermatologist. A dermatologist is a doc who specializes in diseases of the skin. Also, some plastic surgeons, general surgeons, internists, cancer specialists, and family unit doctors have special training in moles and melanoma.
What factors increase the chance of melanoma?
Although anyone can develop melanoma, people with the following run a risk factors accept an increased chance of melanoma (1):
-
Having a dysplastic nevus.
-
Having more than 50 common moles.
-
Sunlight : Sunlight is a source of UV radiation, which causes skin damage that tin lead to melanoma and other skin cancers.
-
Severe, baking sunburns : People who have had at least one astringent, blistering sunburn have an increased chance of melanoma. Although people who fire easily are more likely to accept had sunburns every bit a kid, sunburns during adulthood also increment the chance of melanoma.
-
Lifetime sunday exposure : The greater the full amount of sun exposure over a lifetime, the greater the gamble of melanoma.
-
Tanning : Although having peel that tans well lowers the gamble of sunburn, even people who tan well without sunburning increment their take chances of melanoma by spending time in the dominicus without protection.
Sunlight can be reflected past sand, water, snow, ice, and pavement. The sun's rays tin can become through clouds, windshields, windows, and light wear.
In the United States, pare cancer is more common where the lord's day is strong. For example, a larger proportion of people in Texas than Minnesota get pare cancer. Also, the sunday is potent at higher elevations, such as in the mountains.
-
-
Sunlamps and tanning booths : UV radiation from artificial sources, such as sunlamps and tanning booths, can cause skin damage and melanoma. Health care providers strongly encourage people, particularly young people, to avoid using sunlamps and tanning booths. The run a risk of skin cancer is profoundly increased by using sunlamps and tanning booths earlier historic period 30.
-
Personal history : People who have had melanoma accept an increased take a chance of developing other melanomas.
-
Family histor y: Melanoma sometimes runs in families. People who have ii or more than close relatives (mother, begetter, sis, brother, or child) with melanoma accept an increased hazard of melanoma. In rare cases, members of a family will have an inherited disorder, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, that makes the skin extremely sensitive to the sun and profoundly increases the gamble of melanoma.
-
Pare that burns easily : People who accept fair (pale) peel that burns easily in the sunday, blue or gray eyes, cerise or blond pilus, or many freckles have an increased chance of melanoma.
- Certain medical weather or medicines : Medical conditions or medicines (such every bit some antibiotics, hormones, or antidepressants) that make skin more sensitive to the sun or that suppress the allowed organisation increase the take chances of melanoma.
How can people protect their skin from the sunday?
People can protect their skin from the sun by following the tips on NCI's Sunlight risk cistron page. The best way to prevent melanoma is to limit exposure to sunlight. Having a suntan or sunburn means that the skin has been damaged by the sunday, and connected tanning or burning increases the hazard of developing melanoma.
Source: https://www.cancer.gov/types/skin/moles-fact-sheet
0 Response to "Mole Going From Flat to Bumpy to Flat Again"
Postar um comentário